Lab Architecture¶
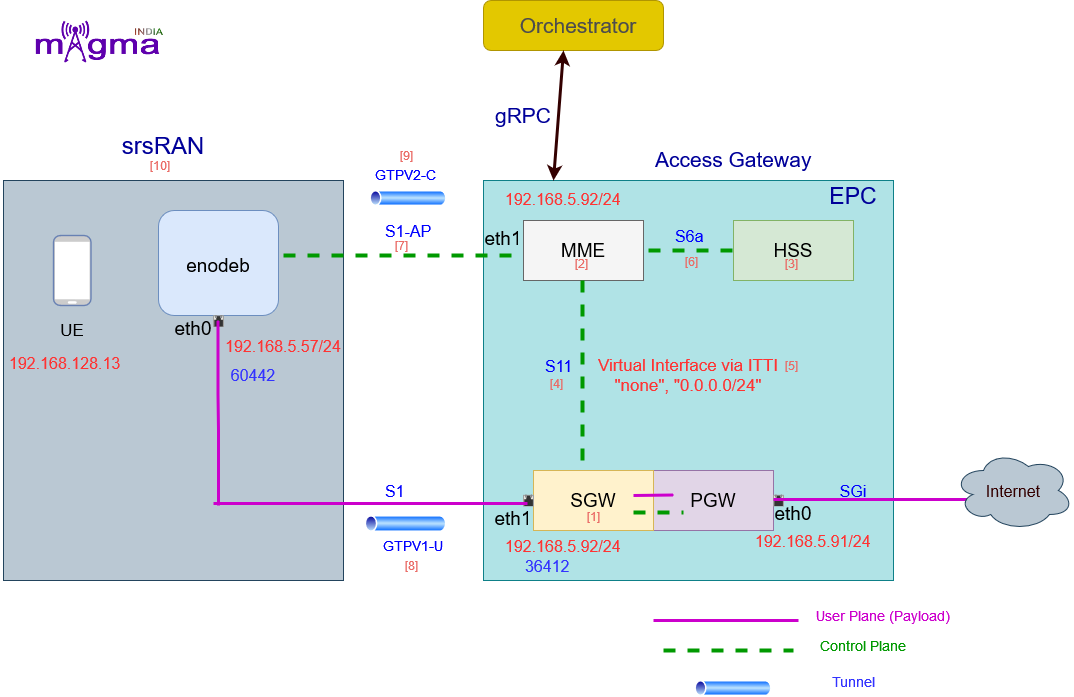
Infra Architecture¶
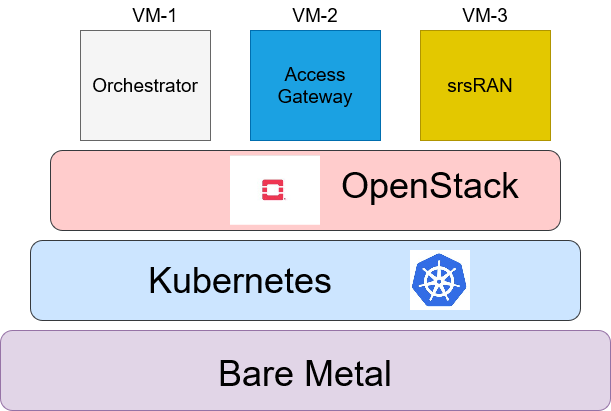
Modules¶
1. PGW ( PDN Gateway )¶
PGW is the network node that connects the EPC to external IP networks. What the PGW does is that it routes packets to and from external IP networks. Beyond that, it also allocates an IP address to all UEs and enforces different policies regarding IP user traffic such as packet filtering.
2. SGW ( Serving Gateway )¶
In order to eliminate any effect on user-data while the UE moves between different eNodeB’s, the SGW works as an anchor point for user-data of the UE, while the UE is moving between different eNodeB’s. In addition, the SGW forwards user data between the eNodeB and the PGW.
[1] ( https://github.com/magma/magma/tree/master/lte/gateway/c/core/oai/tasks/sgw )
3. MME ( Mobility Management Entity )¶
It is used to authenticate the UE. In addition, it tracks the location of the UE. Also, it selects the suitable Serving Gateway and PDN Gateway that would serve this UE.
[2] ( https://github.com/magma/magma/tree/master/lte/gateway/c/core/oai/oai_mme )
4. HSS ( Home Subscriber Server)¶
It is the main subscriber database used within the IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) which provides details of the subscribers to other entities within the network. The IMS enables users to be granted or refused access to other services depending on their status.
[3] ( https://github.com/magma/magma/tree/master/lte/cloud/go/services/subscriberdb )
5. eNodeB¶
It is a 4G site that the UE connects to. It provides a radio interface to UE. It is the hardware that is connected to the mobile phone network that communicates directly wirelessly with mobile handsets (UE).
6. UE ( User Equipment )¶
It is any device used directly by an end-user to communicate. It can be a hand-held telephone, a laptop equipped with a mobile broadband adapter, or any other device. It connects to the base station eNodeB.
7. SGi¶
This interface is used between PGW and intranet or internet. This interface is equivalent to the Gi interface of GPRS.
8. S11¶
This control plane interface S11 is used between MME and SGW for EPS Management.
[4] ( https://github.com/magma/magma/tree/master/lte/gateway/c/core/oai/tasks/s11 )
9. ITTI¶
Inter Task Interface is used for sending messages between tasks
[5] ( https://github.com/magma/magma/tree/master/lte/gateway/c/core/oai/lib/itti )
10. S6a¶
This is the interface between MME and HSS. It is used for the transport of subscriptions, authentications, and authorizations of users.
[6] ( https://github.com/magma/magma/tree/master/lte/gateway/c/core/oai/tasks/s6a )
11. S1-AP¶
The S1 Application Protocol (S1AP) provides the control plane signaling between srsRAN and evolved packet core (EPC).
[7] ( https://github.com/magma/magma/tree/master/lte/gateway/c/core/oai/tasks/s1ap )
12. S1¶
Interface for S1-user plane data for each bearer between the srsRAN and serving gateway. It enables the serving gateway to anchor inter eNodeB handover.
13. Gtpv1-u¶
It is a protocol used to exchange user data over GTP tunnels across the Sx interfaces. An IP packet for a UE (user endpoint) is encapsulated in a GTPv1-U packet and tunneled between the P-GW and the eNodeB for transmission with respect to a UE over S1-U and S5/S8 interfaces.
[8] ( https://github.com/magma/magma/tree/master/lte/gateway/c/core/oai/tasks/gtpv1-u )
14. Gtpv2-c¶
It is a protocol responsible for creating, maintaining and deleting tunnels on multiple Sx interfaces. It is used for control plane path management, tunnel management and mobility management. It also controls forwarding relocation messages; SRNS context and creating forward tunnels during inter LTE handovers.
[9] ( https://github.com/magma/magma/tree/master/lte/gateway/c/core/oai/lib/gtpv2-c )
14. srsRAN¶
srsRAN is a 4G/5G software radio suite.
[10] ( https://github.com/ShubhamTatvamasi/srsRAN-demo )